China Joined Hague Apostille Convention
On March 8, 2023, China submitted its instrument of accession to the Convention of 5 October 1961 Abolishing the Requirement of Legalisation for Foreign Public Documents, also known as Hague Apostille Convention. The Convention will come into force for China on Nov. 7, 2023. China’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MFA) has been designated as the Competent Authority in China’s mainland to issue Apostilles. China’s MFA also authorizes the Foreign Affairs Offices of provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government to issue Apostilles for documents that are issued within their respective administrative areas.
Hague Apostille Convention was made in the Hague, the Netherlands, by the Hague Conference on Private International Law (Hague Conference) in 1961. Since then, more than 120 countries have joined the Hague Apostille Convention. A list of the countries that are contracting parties to Hague Apostille Convention is available on the Hague Conference website.
The purpose of Hague Apostille Convention is to simplify the procedures by which public documents are certified for use abroad. It replaces the traditional legalization/authentication with a single certification known as “Apostille“. The traditional legalization process involves the authorities of the country where the document was issued as well as the Embassy or Consulate of the country where the document is to be used.
Hague Apostille Convention has its limitations. Only countries that are parties to the Convention can issue and accept Apostilles. For other countries, the traditional legalization with embassies and consulates remains in use. The scope of the Convention only covers court documents, administrative documents, notarial acts, and some official certificates. Specific examples are found in The ABCs of Apostilles which is the Hague Convention’s official brochure providing the basic information about Hague Apostille Convention. Also, an Apostille does not certify the content of the document. It only certifies the signature or seal of the person or authority who signed or sealed the document.
How to do Apostille in China
Individuals and businesses that are engaged in cross-border activities (e.g. immigration, work/study abroad, international trade) often need to show public documents issued in one country to officials in another country. An Apostille is a certificate issued by the country of origin to authenticate the stamp, seal, or signature on a public document to be used abroad.
On Nov. 7, 2023, the Convention of 5 October 1961 Abolishing the Requirement of Legalisation for Foreign Public Documents, also known as Apostille Convention or Hague Convention, came into force for China. Since then, China has begun issuing and accepting Apostilles. This article explains the basics of getting an Apostille in China. For more background information about Apostilles, please read our article Understanding Apostille.
Where to Apply for an Apostille in China
The Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MFO) of China is the competent authority for issuing Apostilles for public documents issued in China’s mainland. Although the Consular Department of MFA operates a service window for receiving Apostille applications, most applications are submitted to the designated foreign affairs offices (FAOs) or the entrusted organizations in Beijing. The contact information of the MFA service window, designated FAOs and the entrusted organizations is available in the Apostille Section on the China Consular Service Website (in Chinese).
The entrusted organizations in Beijing who act on behalf of MFA can process Apostilles for documents regardless of where the documents are issued, but each local FAO has a specific administrative jurisdiction meaning it can only deal with the documents issued within its jurisdiction. Suppose you live in a city other than Beijing. To find out where to submit your Apostille application, you can check the list of the designated FAOs in the Apostille Section on the China Consular Service Website and see if there’s a designated FAO in your city. If yes, this FAO is likely to be the most convenient office for filing your Apostille application. If not, then look for the FAOs in the other cities of the same province. The FAOs in the other provinces are irrelevant because they do not have jurisdiction over the documents issued in your province. If you know someone in Beijing who can help, you can always send your document to Beijing for filing the Apostille application. Note that the service window operated by MFA’s consular department currently does not allow third parties to submit applications.
What Documents Can be Apostilled in China
In China, three categories of documents can be apostilled: (1) civil documents notarized by a Chinese notary office, (2) commercial documents certified by the China Council for the Promotion of International Trade (CCPIT), and (3) certain certificates issued by local exit-entry inspection and quarantine bureaus for purposes of exportation. In other words, the documents for which an Apostille can be issued by an FAO in China must bear the stamp of a notary office, CCPIT, or an exit-entry inspection and quarantine bureau. Each of the three categories includes a variety of documents. If you are not sure about whether a particular document can be apostilled in China, you should contact the relevant authorities in the chain of the Apostille process. Below are listed some common documents that can be apostilled in China.
(1) Notarial Civil Documents (Note that all civil documents need to be notarized before they can be apostilled.)
- Certificate of No Criminal Record
- Birth certificate
- Marriage certificate
- Power of attorney
- Educational diploma and transcripts
- Contract
(2) Commercial Documents Certified by CCPIT (Note that all commercial documents need to be certified by CCPIT before they can be apostilled.)
- Certificate of Origin
- Certificate of Free Sale
- Commercial invoice
- Business license
- Customs Declaration Form
- Power of attorney
(3) Exportation-Relevant Certificates issued by Exit-Entry Inspection and Quarantine Bureau
- Certificate of Origin
- Phytosanitary Certificate
- Animal Health Certificate
What Documents Are Required for Applying for an Apostille in China
Typically, when you apply for an Apostille in China, only two documents are required: your original valid identity document and the document that needs to be apostilled. The acceptable identity documents include a China ID card, passport, Mainland Travel Permit for Hong Kong and Macao and Residents, and Mainland Travel Permit for Taiwan Residents. A power of attorney is commonly not required if a third party files the Apostille application.
Additional document(s) are required If the applicant is not a regular individual but rather one of the following: national government-sponsored personnel or student going abroad, enterprise, and diplomatic organization. Also, the Consular Department of MFA has the power to request any documents it deems necessary. More details about the additional documents are available in the Apostille Section on the China Consular Service Website.
How Long Does the Apostille Application Take in China
2-4 working days. In some cases, the local FAO to which the application is submitted does not have the authority to issue an Apostille. Such an FAO needs to use a courier service to send the document to another FAO and later receive it when returned. The 2-4 working days do not cover the courier time in such a case.
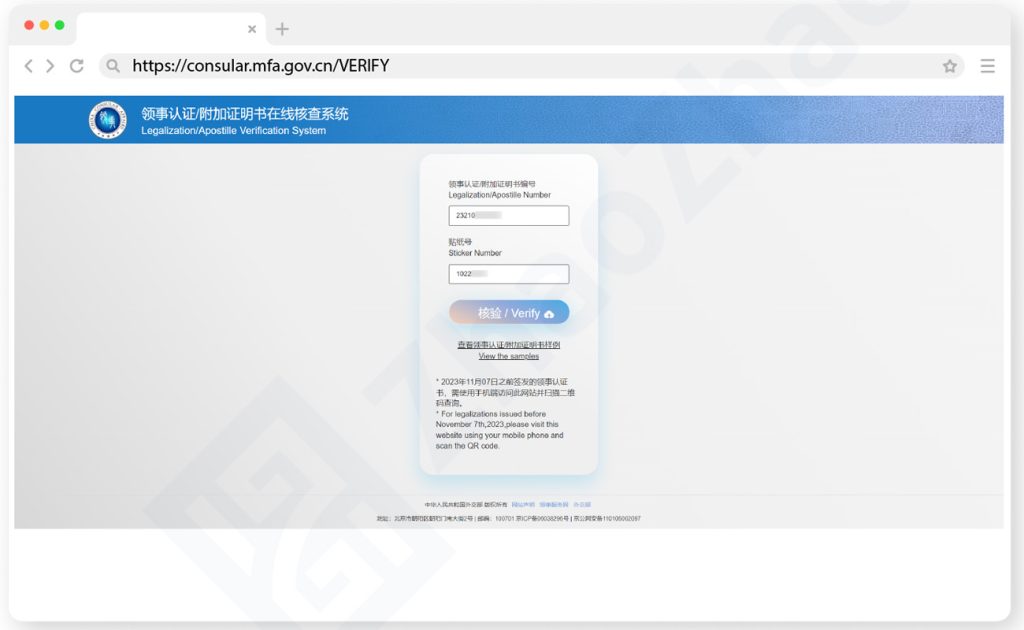
How to Verify an Apostille Issued in China
An Apostille issued in China can be verified by using a cellphone browser or desktop browser. Using a cellphone browser is recommended as it takes scanning a QR code rather than entering some verification numbers manually. Below are illustrations of the two verification methods.
Method One (Recommended)
- Open a browser app on your cellphone and go to the Verification Section on the China Consular Service Website at https://consular.mfa.gov.cn/VERIFY.
- Click “Scan the QR code” and scan the QR code that appears in the top left corner of the Apostille.
- View the verification result.

Method Two
- Open a web browser on your desktop computer or laptop and go to the Verification Section on the China Consular Service Website at https://consular.mfa.gov.cn/VERIFY.
- Enter the Apostille Number and the Sticker Number found in the Apostille. Then, click “Verify”. (See the Sample Apostille showing where to find these numbers).
- View the verification result.
Sample Apostille Issued in China
